Applications Notes / Bulletins
Trokut Solutions caters to widest range of applications in the field of Scientific Research and Industry
Browse PhotoVoltaic Technical Bulletins
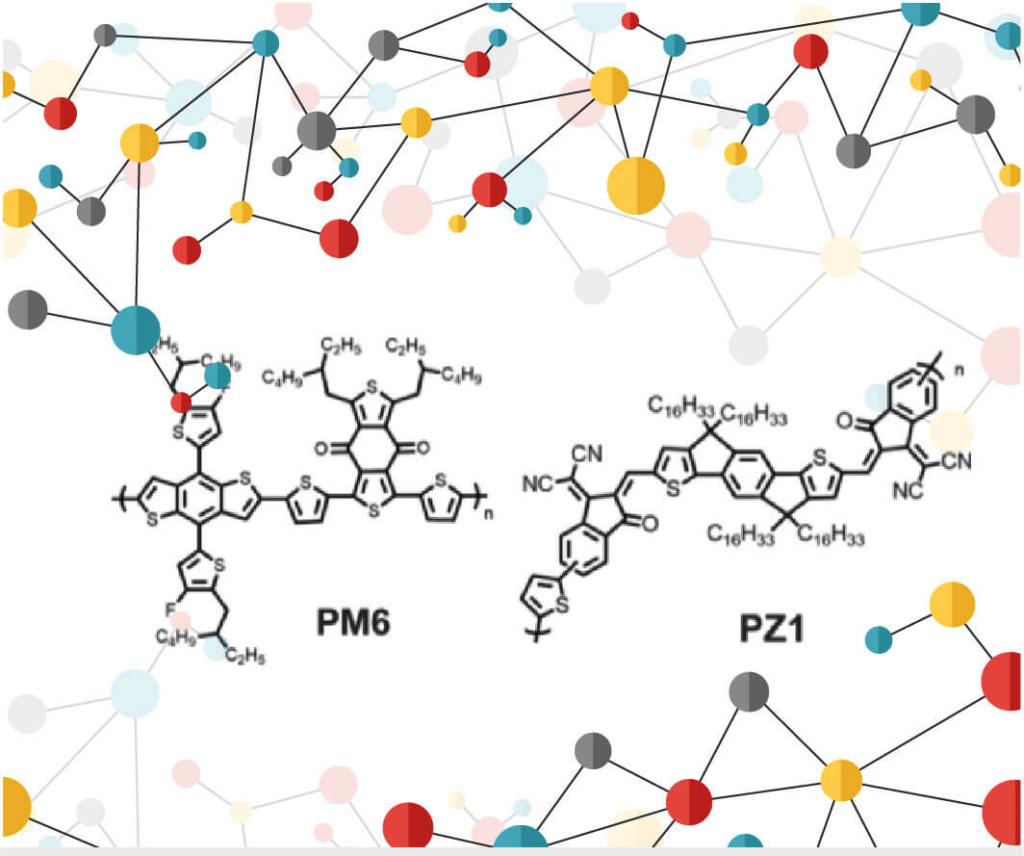
Materials scientists from the Soochow University in China have fabricated all-polymer solar cells (all-PSCs) with 11.2% high efficiency.
Among various strategies to develop the high efficiency conjugated donor polymers, the substitution of fluorine atoms on the conjugated polymer backbone has attracted considerable attention recently, due to the simultaneous lowering of the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) without sacrificing the bandgap, enhanced molecular ordering, high extinction coefficient, and the ability to tune the blend morphology to reduce the charge carrier recombination..
Single junction all-polymer solar cells with high efficiency of 11.2%
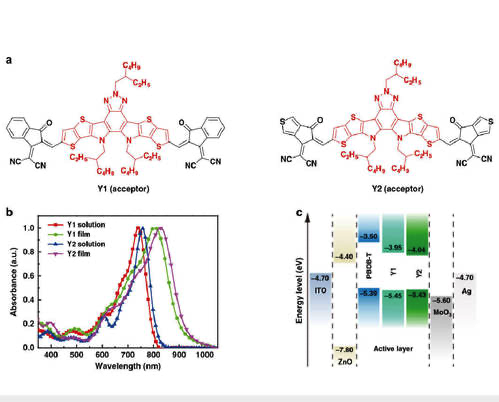
In an advance that makes more efficient in organic photovoltaics (OPVs), University of Central South researchers, Prof. Yingping Zou have developed non-fullerene acceptor organic photovoltaics (NFA-OPV) devices that can achieve 15.7% efficiency. The research was published in Joule and has been heated discussion on the OPVs field.
Before that research came out, Prof. Yingping Zou cooperated with Prof. Yang Yang from UCLA, and Prof. Feng Gao from Linköping University reported a successful strategy to tune the optoelectronic properties by introducing electron-deficient-core-based fused structure into non-fullerene acceptors.
New Strategy for fullerene-free OPVs: Achieving low voltage loss and high photocurrent

Scientists at the Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University have presented a family of near-infrared nonfullerene acceptors (NIR NFA, T1-T4) with fluorinated regioisomeric A–Aπ–D–Aπ–A backbones for constructing efficient single-junction and tandem PSCs with photon response up to 1000 nm.
With the rapid development of new electroactive molecules, the polymer solar cells has experienced fast breakthrough over the past few years. The promising virtue for PSCs is their functional tunabilities stemming from the chemical versatility of organic semiconductors which allows their production in large quantities at relatively low price.
For instance, the recent development of near-infrared (NIR) organics (bandgap, Eg < 1.4 eV) enables PSCs with strong NIR photon responsiveness and visible-range transparency, which are promising for constructing tandem and semitransparent PSCs.
Recent progress in Polymer Solar Cell: Breakthrough Efficiency of 14.64%

The perovskite film with optimized orientation and grain size is desired in fabricating high performance PVSCs. Enlarging the grain size of perovskite polycrystalline film can reduce the grain boundaries, which are regarded as non-radiative recombination centers for photogenerated charge carriers and harmful to charge transport. For the 2D perovskite film, the impact of crystal orientation and grain size will be more significant on the device performance, because of the anisotropy in crystal structure and the resulting anisotropic movement of the charge carriers.
2D perovskite materials could hold key to develop higher efficiency solar cell.

Understanding the I-V characteristic of the internal structure of device is fundamental to develop a highly efficient and highly stable solar cell.
When measuring I-V characteristic in a p-n diode one needs to consider the diffusion current, recombination current and series resistance effects, which could result in the device’s performance. Therefore, researchers could know whether the device is parallel to an ideal diode by calculating the ideality factor η.
The ideality factor η is a number between 1 and 2.
How to analyze the defects in perovskite devices and measure diode ideality factor?
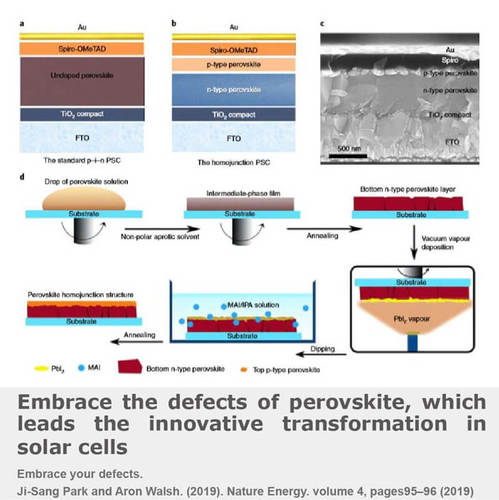
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have emerged as an attractive photovoltaic technology, thanks to their outstanding power conversion efficiency (PCE). Further improvement in the device efficiency is limited by the recombination of the charge carriers in the perovskite layer even when employing heterojunction-based architectures. The team of Prof. Meicheng Li proposed and demonstrated a p-type perovskite/n-type perovskite homojunction whose built-in electric field promotes oriented transport of the photo-induced carriers, thus reducing carrier recombination losses..
Embrace the defects of perovskite, which leads the innovative transformation in solar cells

Prof. Qi Chen, Beijing Institute of Technology, and other materials scientists have developed the high efficiency perovskite films with 20.7 % PCEs, which is certified by NIM, China, by modulating the status of residual strains in controllable manner via rational strain engineering. The mixed halide perovskites have emerged as outstanding light absorbers for efficient solar cells. But it reveals inhomogeneity in these polycrystalline films due to composition separation, which leads to local lattice mismatches and emergent residual strains consequently.
Strain engineering, a new way to break through the efficiency of perovskite
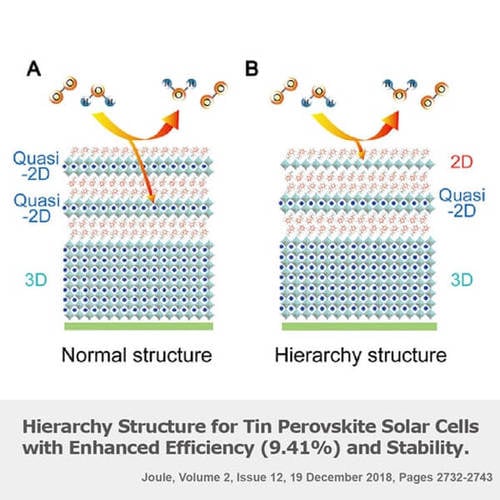
Toxicity and instability of Pb-based PSCs remains to be issues that limit their large-scale application. A bunch of Pb-free PSCs based on elements such as tin (Sn), germanium (Ge), bismuth (Bi), stibium (Sb), and copper (Cu) have been investigated.
A team led by Prof. Zhijun Ning, at ShanghaiTech University, fabricated a Sn-based hierarchy structure perovskite in a one-step process, comprising highly parallel-orientation 2D PEA2Snl4 on the surface of 3D FASnl3. The hierarchy structure delivers significant enhanced stability and oxidation resistance in air atmosphere. They have developed a Sn-based perovskite films in planar structure solar cells and achieved a PCE up to 9.41 %.
2D-Quasi-2D-3D Hierarchy Structure for Tin Perovskite Solar Cells with Enhanced Efficiency (9.41%) and Stability

To improve the brightness, contrast and resolution of the display, while reducing costs and the usage of limited resources, scientists have developed different kinds of light-emitting diodes, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), quantum dots LEDs (QLEDs), perovskite-based LEDs (PVSK LEDs) and micro LEDs. Compared to OLEDs, which are widely used in high-end consumer-electronics, the external quantum efficiency of perovskite-based LEDs has rapidly been improved from 0.76 % to 20.7 % in just four years.
Keywords :
- Perovskite LEDs .
- Improved efficiency.
- Hallide PVSK based LED.
Perovskite-based LEDs are making rapid progress! EQE up to 20.1% comparable to OLEDs

Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are the main alternative to traditional light sources, and perovskite light-emitting devices plays the key role in the light-emitting field. Although it is not so easy to get into the light-emitting device field; however, LEDs based on metal halide perovskite materials have extraordinary characteristics: narrow emission line widths at high photo-luminescence quantum yield (PLQY), high color purity, and color tunable. It can be made at low cost via facile solution processing and be adopted in flat panel display and solid-state lighting applications. Therefore, perovskite LEDs are able to get into the contest of light-emitting devices with organic LEDs (OLEDs) and inorganic quantum dot LEDs (QLEDs).
Keywords :
- Perovskite LEDs .
- Improved efficiency.
- Hallide PVSK based LED.
The key elements to measure higher efficiency of perovskite LED devices

Nature Publishing Group highly recommends authors of papers related to solar-cell research complete this solar checklist of submitted information to aid the reproducibility and transparency of results.
Following discussion with experts in the photovoltaic community and the publication of several articles on the topic of mischaracterization of solar cell efficiency, Nature Photonics (along with other physical science research journals published by Nature Publishing Group) is introducing a checklist for papers submitted on the topic.
( http://www.nature.com/authors/policies/solarchecklist.pdf )
Keywords :
- Solar Characterization .
- Natue Check list for paper submission.
